The Department of Conservation (DOC) is asking visitors to Nelson Lakes National Park this summer to help to protect its pristine alpine lakes from an alga that causes mucus-like ‘lake snow’.
The microscopic alga Lindavia that causes the sticky substance is present in the park’s Lake Rotoiti and Lake Rotoroa.
DOC is working to prevent it being spread to Rotomairewhenua/Blue Lake, Rotomaninitua/Lake Angelus and Rotopōhueroa /Lake Constance and to alpine tarns.
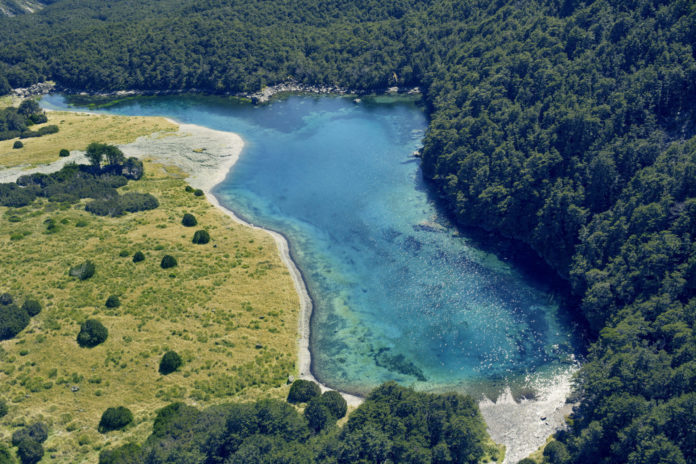
Rotomairewhenua is thought to have the clearest freshwater in the world. To help safeguard the lake and other lakes, hut wardens are at the busy Blue Lake Hut over the summer peak visitor season to speak to trampers about preventing the spread of Lindavia and other aquatic pests, DOC said in a statement.
Rotomairewhenua and Rotopōhueroa are tapu/sacred to Ngāti Apa ki te Rā Tō iwi, and people are being asked not to touch the water in these lakes to uphold their mauri/life force and pureness.
“The Blue Lake hut wardens are talking with visitors about respecting the sacredness of Rotomairewhenua and Rotopōhueroa lakes by not touching the water or swimming in these lakes,” says DOC Community Ranger, Sandra Wotherspoon.
“People shouldn’t wash or put anything in the lakes, including not filling drink bottles.
“This will also help protect Blue Lake’s outstanding water clarity from being ruined by lake snow.
“Already this summer, there have been up to 50 people staying at the hut and campsite some nights – both international and Kiwi trampers. Shep has been really happy so far with the respect and understanding trampers are showing for the lakes.”
Trampers are being asked to make sure all gear has been cleaned and is completely dry before swimming or taking water from Lake Angelus and other tarns. There are no known control or eradication methods for Lindavia, so preventing its spread is a priority, said Ranger Wotherspoon.
“As Lindavia is a microscopic organism, it can be spread to a new area in just one drop of water. Clothing, boots, drink bottles and swimming, tramping and fishing gear could harbour Lindavia. It could then be washed out when entering a different lake or river,” she said.
“Lindavia is a tricky alga. It floats just below the surface and is hard to detect unless it multiplies in a bloom. When it’s not blooming, people won’t even know there’s contamination though the alga will be present.
“We’re asking people to Check, Clean, Dry any clothing and gear that comes into contact with freshwater between every waterway and every waterbody every time in Nelson Lakes and in other areas to protect their water quality and aquatic life.”
She said lake snow hangs under the water and can stick to fishing gear, boats, motors, and people. It’s not known how Lindavia will affect the ecology and health of the lakes. It is not toxic to humans or livestock and poses no risk from food sourced from the lakes, the ranger said.